| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2014-08-29 05:02:02 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:26:37 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D4068 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | C-Curarine |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | C-Curarine is a Curare alkaloid that is structurally similar to D-tubocurarine. Curare is a non-depolarizing muscle relaxant that blocks the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR), one of the two types of acetylcholine (ACh) receptors, at the neuromuscular junction. The main toxin of curare, D-tubocurarine, occupies the same position on the receptor as ACh with an equal or greater affinity making it a competitive antagonist. |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Amine
- Ether
- Natural Compound
- Organic Compound
- Plant Toxin
|
|---|
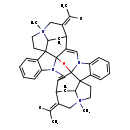
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | |
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C40H44N4O |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 596.803 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 596.350 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 7168-64-1 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (30Z,38Z)-30,38-diethylidene-16,32-dimethyl-10-oxa-8,16,26,32-tetraazadodecacyclo[27.5.2.2¹³,¹⁶.1⁸,¹².0¹,⁹.0²,⁷.0⁹,²⁸.0¹¹,¹⁹.0¹¹,²⁶.0¹⁵,¹⁹.0²⁰,²⁵.0³²,³⁵]nonatriaconta-2,4,6,12(39),20,22,24,27-octaene-16,32-diium |
|---|
| Traditional Name | (30Z,38Z)-30,38-diethylidene-16,32-dimethyl-10-oxa-8,16,26,32-tetraazadodecacyclo[27.5.2.2¹³,¹⁶.1⁸,¹².0¹,⁹.0²,⁷.0⁹,²⁸.0¹¹,¹⁹.0¹¹,²⁶.0¹⁵,¹⁹.0²⁰,²⁵.0³²,³⁵]nonatriaconta-2,4,6,12(39),20,22,24,27-octaene-16,32-diium |
|---|
| SMILES | [H]\C(C)=C1\C[N+]2(C)CCC34C2CC1C1=CN2C5=CC=CC=C5C56CC[N+]7(C)C\C(=C(\[H])C)C(CC57)C5=CN(C7=CC=CC=C37)C41OC265 |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1/C40H44N4O/c1-5-25-23-43(3)17-15-37-29-11-7-10-14-34(29)42-22-32-28-20-36-38(16-18-44(36,4)24-26(28)6-2)30-12-8-9-13-33(30)41-21-31(27(25)19-35(37)43)39(37,42)45-40(32,38)41/h5-14,21-22,27-28,35-36H,15-20,23-24H2,1-4H3/q+2/b25-5+,26-6+ |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=DWELRYDMYVJVSL-GQBJSJAWNA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as strychnos alkaloids. These are alkaloids having a core structure based on the strychnan, stemmadenine (seco-curan), or the akuammicine (curan) skeleton. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Alkaloids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Strychnos alkaloids |
|---|
| Sub Class | Not Available |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Strychnos alkaloids |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Strychnan skeleton
- Akuammicine-skeleton
- Stemmadenine-skeleton
- Curan skeleton
- Carbazole
- Indolizidine
- Indole or derivatives
- Aralkylamine
- Benzenoid
- N-alkylpyrrolidine
- Piperidine
- Tetraalkylammonium salt
- Quaternary ammonium salt
- Pyrrolidine
- Oxacycle
- Azacycle
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Enamine
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic salt
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Amine
- Organic cation
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | Not Available |
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Not Available |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | It has been prpoposed that surarine speeds up destruction of chemical transmitter, and raises the threshold point at which excess of the transmitter is able to exert its depressant power. (1) |
|---|
| Metabolism | Not Available |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | The main toxin of curare, D-tubocurarine, occupies the same position on the receptor as ACh with an equal or greater affinity making it a competitive antagonist. |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Not Available |
|---|
| Symptoms | Not Available |
|---|
| Treatment | Not Available |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| HMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 6391813 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | 16735754 |
|---|
| KEGG ID | C09144 |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| CTD ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ACToR ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | - Briscoe G: The antagonism between curarine and acetylcholine. J Physiol. 1936 Sep 8;87(4):425-8. [16994803 ]
|
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|