| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2014-08-29 05:01:22 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:26:37 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D4066 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Ryanodine |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
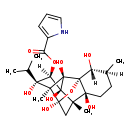
| Description | Ryanodine is a poisonous alkaloid found in the South American plant Ryania speciosa (Flacourtiaceae). It was originally used as an insecticide. The compound has extremely high affinity to the open-form ryanodine receptor, a group of calcium channels found in skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, and heart muscle cells. It binds with such high affinity to the receptor that it was used as a label for the first purification of that class of ion channels and gave its name to it. |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Ester
- Insecticide
- Natural Compound
- Organic Compound
- Pesticide
- Plant Toxin
|
|---|
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | |
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C25H35NO9 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 493.547 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 493.231 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 15662-33-6 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (1R,2R,3S,6S,7S,9S,10S,11S,12R,13S,14R)-2,6,9,11,13,14-hexahydroxy-3,7,10-trimethyl-11-(propan-2-yl)-15-oxapentacyclo[7.5.1.0¹,⁶.0⁷,¹³.0¹⁰,¹⁴]pentadecan-12-yl 1H-pyrrole-2-carboxylate |
|---|
| Traditional Name | ryania |
|---|
| SMILES | [H][C@@]1(OC(=O)C2=CC=CN2)[C@](O)(C(C)C)[C@]2(C)[C@]3(O)C[C@@]4(C)[C@@]5(O)CC[C@]([H])(C)[C@@]([H])(O)[C@]5(O3)[C@]2(O)[C@@]14O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C25H35NO9/c1-12(2)22(31)17(34-16(28)14-7-6-10-26-14)23(32)18(4)11-21(30)19(22,5)25(23,33)24(35-21)15(27)13(3)8-9-20(18,24)29/h6-7,10,12-13,15,17,26-27,29-33H,8-9,11H2,1-5H3/t13-,15+,17+,18-,19-,20-,21-,22+,23+,24+,25+/m0/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=JJSYXNQGLHBRRK-YSOSZROBSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as diterpenoids. These are terpene compounds formed by four isoprene units. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Prenol lipids |
|---|
| Sub Class | Diterpenoids |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Diterpenoids |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Diterpenoid
- Ryanodane diterpenoid
- Pyrrole-2-carboxylic acid or derivatives
- Oxepane
- Monosaccharide
- Oxane
- Substituted pyrrole
- Cyclic alcohol
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Pyrrole
- Tetrahydrofuran
- Tertiary alcohol
- Carboxylic acid ester
- Hemiacetal
- Secondary alcohol
- Polyol
- Oxacycle
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Azacycle
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organic oxide
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Alcohol
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | - Actin Cytoskeleton
- Actin Filament
- Caveolae
- Cell junction
- Cell surface
- Cytoplasm
- Cytoskeleton
- Cytosol
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Endoplasmic reticulum membrane
- Endosome
- Extracellular
- Golgi apparatus
- Membrane Fraction
- Microsome
- Mitochondrial Matrix
- Mitochondrion
- Nuclear Membrane
- Perinuclear region
- Plasma Membrane
- Sarcoplasm
- Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
- Secretory vesicle
- Synaptic Vesicle
|
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | | Name | SMPDB Link | KEGG Link |
|---|
| Apoptosis | Not Available | map04210 | | Insulin secretion | Not Available | map04911 | | Cardiac muscle contraction | Not Available | map04260 | | Oxidative phosphorylation | Not Available | map00190 | | Circadian rhythm | Not Available | map04710 | | Long-term potentiation | Not Available | map04720 | | Long-term depression | Not Available | map04730 | | Phototransduction | Not Available | map04744 | | Renin-angiotensin system | Not Available | map04614 | | Cholinergic synapse | Not Available | map04725 | | Calcium signaling pathway | Not Available | map04020 | | Antiarrhythmic Drugs | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Applications | |
|---|
| Biological Roles | |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0006-1002900000-c715042aa215c115e2ed | 2016-06-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-000x-8004900000-d44f709b09d0431bc675 | 2016-06-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-014l-9005000000-412616ac99f603b75923 | 2016-06-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0006-1105900000-7da3ccb64cfebdd8793a | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-029y-3309300000-40f8eb8ad8754e0a4063 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-090u-9206000000-1ef5662142d2f1641530 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Not Available |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Ryanodine has extremely high affinity to the open-form ryanodine receptor, a group of calcium channels found in skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, and heart muscle cells. It binds with such high affinity to the receptor that it was used as a label for the first purification of that class of ion channels and gave its name to it. At nanomolar concentrations, ryanodine locks the receptor in a half-open state, whereas it fully closes them at micromolarconcentration. The effect of the nanomolar-level binding is that ryanodine causes release of calcium from calcium stores as thesarcoplasmic reticulum in the cytoplasm, leading to massive muscular contractions. (Wikipedia) |
|---|
| Metabolism | Not Available |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | This is a natural compound that is used as a pesticide. |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Not Available |
|---|
| Symptoms | Not Available |
|---|
| Treatment | Not Available |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| HMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 441753 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | 390355 |
|---|
| KEGG ID | C08705 |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| CTD ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ACToR ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | T3D4066.pdf |
|---|
| General References | Not Available |
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|