| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-07-03 20:54:23 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:25:31 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D2453 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Gyromitrin |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Gyromitrin is found in mushrooms. Toxin from the fungus Gyromitra esculenta. Freq. cause of mushroom poisoning Gyromitrin is a toxin and possible carcinogen present in most members of the fungal genus Gyromitra, most notably the false morel G. esculenta. |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Food Toxin
- Fungal Toxin
- Hydrazine
- Metabolite
- Mycotoxin
- Natural Compound
- Organic Compound
|
|---|
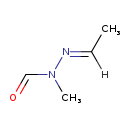
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | | Acetaldehyde formylmethylhydrazone | | Acetaldehyde methylformylhydrazone | | Acetaldehyde N-formyl-N-methylhydrazone | | Acetaldehyde N-methyl-N-formylhydrazone | | Acetaldehyde N-methylformylhydrazone | | Acetaldehyde, N-formyl-N-methylhydrazone | | Acetaldehyde-N-formyl-N-methylhydrazone | | Acetaldehyde-N-methyl-N-formylhydrazone | | Acetylaldehyde-N-methyl-N-formylhydrazone | | Cetaldehyde methylformylhydrazone | | Ethylidene gyromitrin | | Ethylidenemethyl-Hydrazine carboxaldehyde | | Ethylidenemethyl-Hydrazine carboxyaldehyde | | Ethylidenemethyl-Hydrazinecarboxaldehyde | | Ethylidenemethylhydrazinecarboxaldehyde, 9CI | | Formic acid 2-ethylidene-1-methylhydrazide | | Formic acid, 2-ethylidene-1-methylhydrazide | | Formic acid, ethylidenemethylhydrazide | | Hydrazinecarboxaldehyde, ethylidenemethyl- (9CI) | | N'-Ethylidene-N-formyl-N-methylhydrazine | | N'-Ethylidene-N-methylformic hydrazide | | N'-Ethylidene-N-methylformohydrazide | | N'-[(1E)-Ethylidene]-N-methylformic hydrazide | | N'-[-Ethylidene]-N-methylformic hydrazide | | N-Methyl-N-formyl hydrazone of acetaldehyde | | N-Methyl-N-formylhydrazone acetaldehyde |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C4H8N2O |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 100.119 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 100.064 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 16568-02-8 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | N'-[(1E)-ethylidene]-N-methylformohydrazide |
|---|
| Traditional Name | ethylidene gyromitrin |
|---|
| SMILES | [H]\C(C)=N/N(C)C=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C4H8N2O/c1-3-5-6(2)4-7/h3-4H,1-2H3/b5-3+ |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=IMAGWKUTFZRWSB-HWKANZROSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as n-alkylated hydrazones. These are organonitrogen compounds containing a hydrazone group that is substituted with an alkyl group. They have the generic structure RNN=C(R')R\" (R= alkyl group; R',R\"= H or organyl group). |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic nitrogen compounds |
|---|
| Class | Organonitrogen compounds |
|---|
| Sub Class | Hydrazines and derivatives |
|---|
| Direct Parent | N-alkylated hydrazones |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - N-alkylated hydrazone
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Liquid |
|---|
| Appearance | Not Available |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | 19.5°C | | Boiling Point | 143 °C, 416°K, 289 °F | | Solubility | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0udi-1900000000-6886f52c8308abf01476 | 2016-08-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0zfr-9400000000-1512ed65eadbc59fb19f | 2016-08-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-054o-9000000000-4c4b3367f2af862207db | 2016-08-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0002-9000000000-31d6770e020842c1618b | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0595-9000000000-e013bb93be9ce728ea13 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0006-9000000000-4f0872f655ea8b457844 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Oral, dermal, inhalation, and parenteral (contaminated drugs). (1) |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | The toxicity is caused by the conversion of the hydrazine (gyromitrin) to a hydrazine metabolite intermediate monomethylhydrazine. This occurs when gyromitrin begins to be metabolized and it undergoes hydrolysis. The necrosis and steatosis are caused by monomethylhydrazine. (3) |
|---|
| Metabolism | Gyromitrin is converted to a hydrazine metabolite intermediate monomethylhydrazine. This occurs when gyromitrin begins to be metabolized and it undergoes hydrolysis. (3) |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | 3, not classifiable as to its carcinogenicity to humans. (4) |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | Gyromitrin is a toxic and possibly carcinogenic chemical present in most members of the fungal genus Gyromitra, most notably the false morel G. esculenta. (3) |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Consuming large amounts of gyromitrin, such as are found in untreated false morels, may lead to catastrophic liver failure and death. (3) |
|---|
| Symptoms | Initial symptoms of gyromitrin exposure include headache, nausea and dizziness. As gyromitrin is quite volatile, even just the presence of false morels in a poorly ventilated space may be enough to cause these symptoms. (3) |
|---|
| Treatment | Not Available |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB33952 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 5365327 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | 19957776 |
|---|
| KEGG ID | C08305 |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 5583 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| CTD ID | C005666 |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Gyromitrin |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ACToR ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Gyromitrin |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | - Peraica M, Domijan AM: Contamination of food with mycotoxins and human health. Arh Hig Rada Toksikol. 2001 Mar;52(1):23-35. [11370295 ]
- Yannai, Shmuel. (2004) Dictionary of food compounds with CD-ROM: Additives, flavors, and ingredients. Boca Raton: Chapman & Hall/CRC.
- Wikipedia. Gyromitrin. Last Updated 29 May 2009. [Link]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (2014). IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. [Link]
|
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|